Excel’s COUNT Function [With 2 Examples & Troubleshooting!]
Contents
The COUNT Function in Excel quickly counts the number of cells in a range.
It simplifies data analysis by providing a fast way to quantify numeric data in your spreadsheets.
COUNT Function Details
| Available in: | All versions of Microsoft Excel |
| User Level: | Beginners |
| Inputs: | “range”: Cells to be counted. |
| Output: | Number of cells with numeric values. Data Type: Number |
| Wildcards: | Not applicable |
| Case Sensitive: | No |

Where To Find The COUNT Function
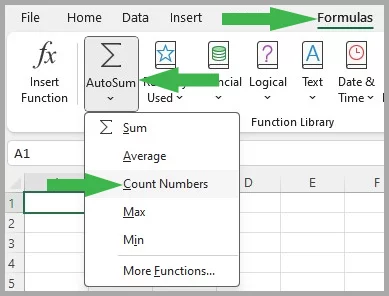
To find the COUNT function, go to the top of the ribbon on your screen.
Click Formulas > AutoSum, and scroll down to the Count Numbers button.
Using COUNT With Other Data Types
COUNT will typically not work with other data types as it requires numbers to function.
However, it does work with currencies, which Excel handles very well.
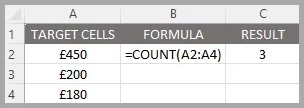
Currency Data:
COUNT can count up currencies since Excel sees them as a number.
Simple Example
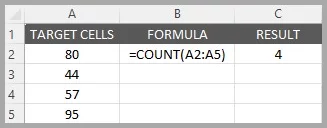
Imagine you have a list of scores from a test in cells A1 to A5 and want to know how many students have taken the test.
You can use the COUNT function to quickly find out the number of scores listed.
Here’s how you do it:
Enter the formula:
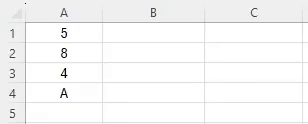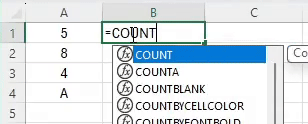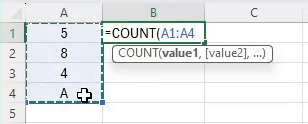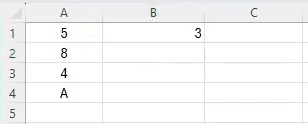
=COUNT(A2:A5)This formula counts the number of cells in the range A1 to A5 that contain numbers, giving you the total number of test scores.
In the real world your data probably won’t be so perfect, using the TRIM function can clean it up for you.
Advanced Example
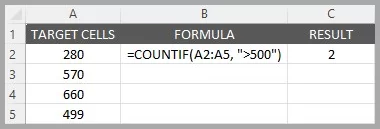
Let’s say you have a list of sales figures for the week in cells B1 to B10 and want to count how many days had sales exceeding $500.
You can use COUNTIF, a version of count that includes a logical function.
Here’s the step-by-step process:
Type in the formula:
=COUNTIF(A2:A5, ">500")This formula checks each cell in the range A2 to A5 and counts only those cells where the value is greater than $500.
The result will tell you the number of days with sales over $500.
This method is particularly useful for quickly assessing performance against a specific target!
Troubleshooting & Errors
Lets take a look at the most common error you will get when working with COUNT.
Error 1: #VALUE! Error
Cause: Non-numeric or non-date data in COUNT range.
Solution: Ensure the range contains only numbers or dates.
Error 2: Lower Count Than Expected
Cause: COUNT only considers numeric values, not text.
Solution: Use COUNTA for a total count including text.
Error 3: #NAME? Error
Cause: Incorrect function name or syntax error.
Solution: Verify the function name and syntax are correct.
What Is The COUNT Function Useful For?
The COUNT function in Excel is incredibly versatile, aiding in various aspects of data management and analysis.
Here’s how it can be applied in everyday Excel tasks:
| 1. Data Validation: | Ensures datasets have the expected number of numeric entries. |
| 2. Data Analysis: | Quickly assesses the quantity of numeric data for analysis. |
| 3. Statistical Calculations: | Forms a basis for more complex statistical functions. |
Functions are the key to unlocking Excel’s potential, learning them is a huge part of our Excel training.
Similar Useful Functions
Other functions similar to the Excel value function that are easy to use include:
- COUNTA: Counts cells containing any type of information.
- COUNTIF: Counts cells based on a specified condition.
- SUM: Adds all values from a range of cells.
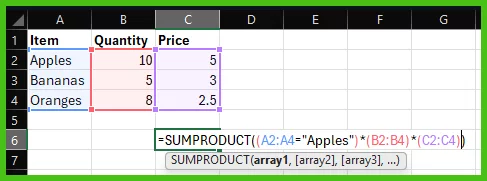
- SUMPRODUCT: Multiplies corresponding numbers in arrays.
Conclusion:
The COUNT function is a fundamental tool in Excel for efficiently counting numeric cells.
It’s essential for data validation, analysis, and forms the basis for more complex calculations.
With its simple usage and powerful applications, COUNT is an indispensable function for Excel users of all levels.